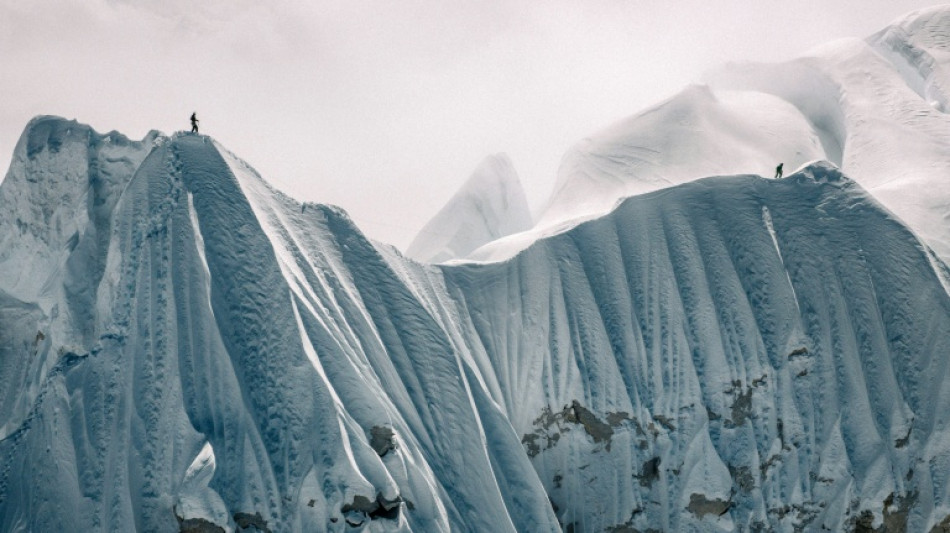
Nepal's 'hidden' mountains draw new wave of climbers
Nepal's mountains including Everest have long drawn climbers from across the world, but a growing community is exploring hidden summits promising solitude and the chance to be first to the top.
The Himalayan nation is home to eight of the world's 10 highest peaks and welcomes hundreds of climbers every year, making mountaineering a lucrative business.
While commercial expeditions dominate on Everest and other 8,000-metre (26,246-foot) giants, a new generation of adventurers is looking sideways rather than upward -- towards the countless 6,000- and 7,000m summits studding Nepal.
The country has 462 peaks open for climbing and around a hundred have never been summited.
"If you are only interested in the height of the peak then there are limited mountains to climb," French alpinist and veteran expedition leader Paulo Grobel told AFP.
"But if you open your interest to 7,900 metres there is a lot of potential. If you go to 6,900 metres you have many more peaks waiting."
This autumn Nepal has issued 1,323 climbing permits.
While most climbers are part of large commercial expeditions on popular peaks, small, independent teams are dispersed across remote and lesser-known mountains.
Many of these expeditions, including French, Japanese and Swiss teams, are tackling summits in true alpine style: minimal support, no supplementary oxygen, no fixed ropes and carrying all their own gear.
The concept is not new but it is rapidly gaining momentum.
- 'Adventure is way bigger' -
"It's a huge challenge," said French mountaineering star Benjamin Vedrines, 33, back from the first ascent of the 7,468m Jannu East with another French climber Nicolas Jean.
"For me, it is very important. Alpine style is completely different in terms of skills, in terms of passion. The adventure is way bigger."
Vedrines believes there are huge possibilities for alpine climbs on Nepali mountains outside the highest peaks.
"They're just lower than 8,000 metres," he said. "Maybe society values them less, but they're underrated. There's so much left to explore."
The shift comes as questions about sustainability, overcrowding and commercialisation reshape mountaineering.
Billi Bierling, who runs the Himalayan Database recording expedition data, said: "With more crowds on the 8000'ers it is actually a beautiful development.
"That young, technically able alpinists are looking at other, more interesting peaks.
"Hopefully it will also be safe because that's the next thing."
- Endless possibilities -
Many of Nepal's mid-range peaks remain logistically out of reach -- not because they are too difficult, but because they are too remote.
"In Nepal, what is challenging is access," said Nepali climber and guide Vinayak Malla, whose team has been nominated for the prestigious Piolets d'Or award for the first ascent of the 6,450m Patrasi Peak last year.
"It is expensive to travel and then you will have to trek to areas where hotels don't exist much," he added. "Rescue is difficult."
On the plus side, smaller expeditions also mean climbers are spread across a wider area, bringing tourism income to valleys that have long remained outside mainstream trekking routes.
In August, Nepal waived climbing fees for 97 mountains to promote lesser-known peaks.
"We are seeing more interest in mountains below 8,000 metres," said Himal Gautam, chief of the mountaineering section at Nepal's tourism department.
"Gradually, we're promoting new regions, so that as interest increases, the infrastructure and manpower needed to support them can develop."
Grobel says it is another part of "Nepal's climbing story".
"If you are interested in the climbing experience, you need to go to the other peaks," he said.
"The possibilities are endless."
F.Eklund--StDgbl